Exploring Plug-In Hybrids: A Simple Guide to P0-P4 Systems
Picture: R. Ellinger and W. Schöffmann
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) are like having the best of both worlds: the eco-friendliness of electric power and the reliability of a traditional engine. But did you know that not all PHEVs are created equal? Depending on how the electric motor and battery interact with the engine, these hybrids come in different types, from P0 to P4. Each type has its own unique way of balancing electric and gasoline power, affecting how the car drives and how efficient it is. In this blog, we’ll break down these five types in a simple, relatable way so you can understand what makes each one tick.
The Different Types of Plug-In Hybrids: A Simple Guide
Imagine you’re at a crossroads, choosing between a sleek, fuel-efficient car and a powerful, reliable gas engine. What if you didn’t have to choose? Enter the world of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), where you get the best of both worlds. But not all PHEVs are alike. Let’s take a road trip through the different types, from P0 to P4, and see how they work.
P0: The Mild-Mannered Hybrid
How It Works:
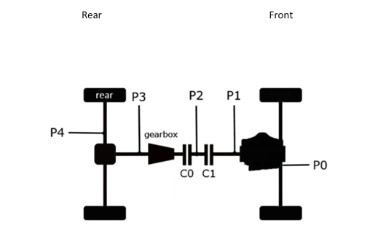
Think of the P0 hybrid as the mild-mannered, helpful sidekick. Here, the electric motor is connected to the engine via a belt, like how a fan belt drives your car’s cooling system. This motor gives the engine a little boost when you accelerate and helps start it up, but it’s not powerful enough to let you drive on electricity alone.
- Pros: This setup is simple and affordable, making it a great way to save fuel without breaking the bank.
- Cons: You won’t be able to drive purely on electric power, and the benefits are modest.
P0 systems are perfect for those who want to dip their toes into hybrid technology without diving all the way in.
P1: The Hybrid with a Little More Pep
How It Works:
The P1 setup is like adding a little pep to your step. Here, the electric motor is placed between the engine and the transmission. It can give you an extra push when you need it and even take over for the engine entirely—though only for short distances.
- Pros: It’s more efficient and can give you a taste of electric driving.
- Cons: Still heavily relies on the gasoline engine, and the electric range is pretty limited.
P1 hybrids offer a nice balance between traditional and electric driving, giving you a bit more flexibility.
P2: The Hybrid That Knows When to Take Charge
How It Works:
Picture the P2 hybrid as a savvy co-pilot who knows when to take the wheel. The electric motor is still between the engine and the transmission, but with a key difference—a clutch can disconnect the engine. This means the motor can power the car on its own, giving you longer stretches of electric-only driving.
- Pros: This system offers smoother transitions and better fuel efficiency, with the ability to drive more often on electric power alone.
- Cons: It’s a bit more complex and can be pricier.
P2 hybrids are for those who want to rely more on electric driving without giving up the safety net of a gasoline engine.
P3: The Performance-Driven Hybrid
How It Works:
If P2 is a savvy co-pilot, P3 is the adrenaline junkie. The electric motor is connected directly to the transmission’s output shaft, meaning it can power the wheels independently of the engine. This setup not only allows for electric-only driving but also delivers a burst of power when you need it most.
- Pros: Strong electric driving capability, especially at higher speeds. It’s a thrill-seeker’s hybrid.
- Cons: More complex and expensive, requiring a larger battery.
P3 systems are for those who want to feel the electric power under their feet while still having the engine’s strength in reserve.
P4: The All-Wheel-Drive Hybrid
How It Works:
Finally, we have the P4 hybrid, the adventurous spirit. Here, the electric motor is placed on the rear axle, separate from the engine and transmission. This setup allows for all-wheel drive (AWD), with the engine powering the front wheels and the electric motor powering the rear.
- Pros: Provides AWD capability, which is great for handling and driving in various conditions. It’s the ultimate hybrid for those who crave performance and versatility.
- Cons: It’s the most complex and costly of the bunch, needing a significant battery.
P4 hybrids are perfect for SUV and crossover drivers who want the confidence of AWD along with the benefits of hybrid technology.
Bringing It All Together
Whether you’re looking for a simple, cost-effective way to save fuel or a high-performance vehicle that can handle any terrain, there’s a plug-in hybrid out there for you. The P0 system gives you a gentle nudge toward better fuel efficiency, while P4 takes you on a thrilling ride with electric AWD capability. Each type offers its own unique blend of electric and gasoline power, making it easier to find a hybrid that fits your lifestyle.
References:
- Wikipedia: Hybrid Vehicle Drivetrain
- CarClarified: The Hybrid drive modes
- ZF: Hybrid Drive – this is how they work
- SAE International. “Understanding Hybrid Drivetrain Configurations”


